Behind the scenes, Power Platform uses Azure subnet delegation and workload injection:
This ensures that traffic to databases, APIs, and private services stays fully inside the enterprise network boundary.
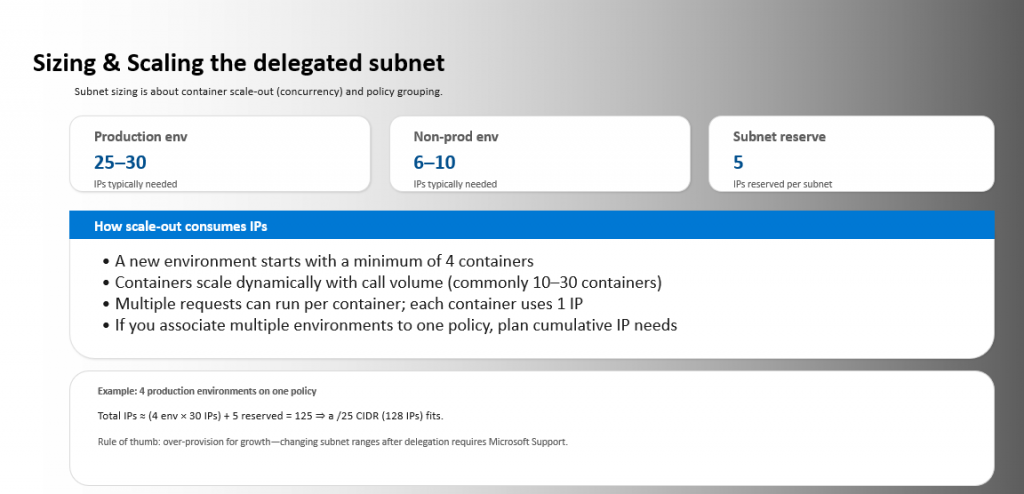
Because containers scale dynamically, subnet sizing must accommodate concurrency:
Over‑provisioning is highly recommended, as changing ranges post‑delegation requires support intervention.
Install-Module Microsoft.PowerPlatform.EnterprisePolicies -Scope CurrentUser -Force
Import-Module Microsoft.PowerPlatform.EnterprisePolicies
$SubscriptionId = “00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000”
$ResourceGroup = “rg-pp-ep-uk”
$VnetNameUKS = “vnet-pp-uksouth”
$SubnetUKS = “snet-pp-delegated”
$VnetNameUKW = “vnet-pp-ukwest”
$SubnetUKW = “snet-pp-delegated”
$VnetAddrUKS = “10.10.0.0/16”
$SubnetAddrUKS = “10.10.1.0/24”
$VnetAddrUKW = “10.20.0.0/16”
$SubnetAddrUKW = “10.20.1.0/24”
New-VnetForSubnetDelegation `
-SubscriptionId $SubscriptionId `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroup `
-CreateVirtualNetwork `
-VirtualNetworkName $VnetNameUKS `
-SubnetName $SubnetUKS `
-AddressPrefix $VnetAddrUKS `
-SubnetPrefix $SubnetAddrUKS `
-Region “uksouth”
New-VnetForSubnetDelegation `
-SubscriptionId $SubscriptionId `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroup `
-CreateVirtualNetwork `
-VirtualNetworkName $VnetNameUKW `
-SubnetName $SubnetUKW `
-AddressPrefix $VnetAddrUKW `
-SubnetPrefix $SubnetAddrUKW `
-Region “ukwest”